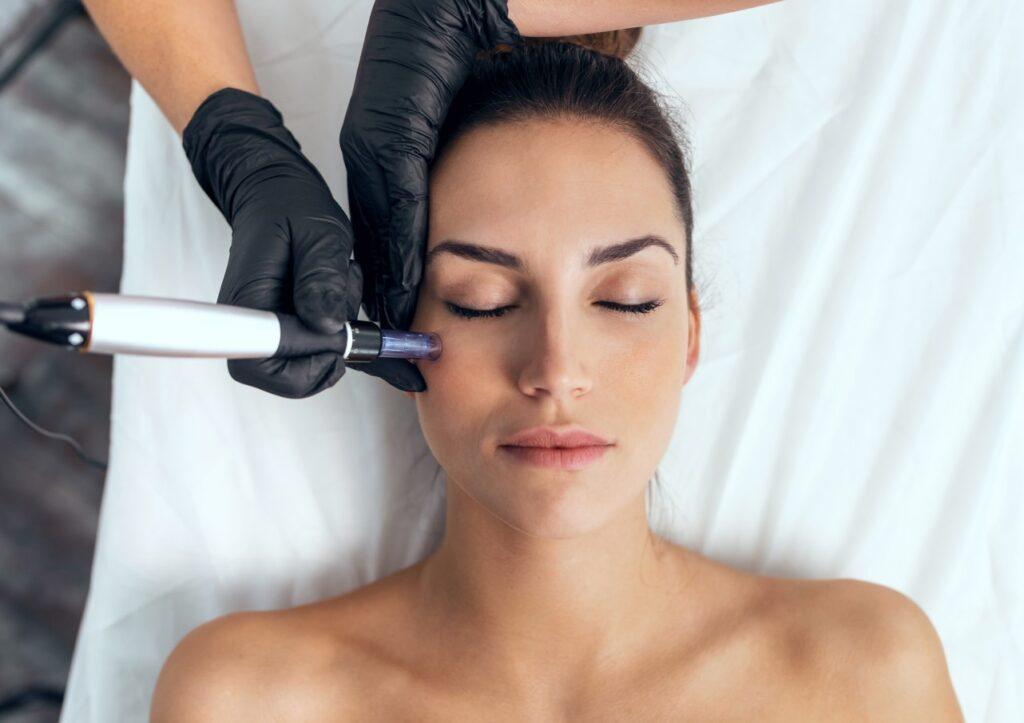
Microneedling: A Revolution in Skin Therapy
Microneedling is a very simple, safe, effective, and minimally invasive therapeutic technique. It was initially introduced for skin rejuvenation and has gained significant attention and popularity more recently. This technique has found applications in a wide range of indications including facial lines and scars to hair loss and hyperpigmentation, microneedling is emerging as a versatile and transformative solution for various dermatological and cosmetic concerns.
The Basics of Microneedling
Microneedling, also known as collagen induction therapy, involves the use of a device equipped with tiny, fine needles that create controlled micro-injuries in the skin’s surface. These micro-injuries stimulate the body’s natural wound healing processes, which, in turn, triggers collagen and elastin production. Collagen and elastin are proteins responsible for maintaining the skin’s structure and elasticity, making microneedling an effective method for skin rejuvenation and repair.
Expanding Applications
While microneedling initially gained recognition for its remarkable effects on skin texture, it has since evolved to address a plethora of dermatological and cosmetic concerns.
Facial Lines and Wrinkles: As the collagen and elastin production is stimulated, microneedling can significantly reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, promoting a more youthful complexion.
Acne Scars and Active Acne: Microneedling can break down scar tissue and stimulate the regeneration of new, healthier skin cells, making it an excellent option for treating both acne scars and active acne.
Post-Traumatic/Burn Scars: For individuals with scars from injuries or burns, microneedling can help improve skin texture and reduce the visibility of scars.
Alopecia: Microneedling has shown promise in stimulating hair growth by increasing blood flow and nutrient delivery to hair follicles. This makes it a potential solution for individuals dealing with alopecia or thinning hair.
Surgical Scars: Post-surgery scars can be softened and smoothed through microneedling, enhancing the overall appearance of the skin.
Hyperpigmentation: Microneedling can aid in breaking down excess melanin, which is responsible for hyperpigmentation issues like melasma or sunspots.
Drug Delivery: Microneedling is also being explored as a method for drug delivery. By creating tiny channels in the skin, it allows for more efficient absorption of topical medications.
Hyperhidrosis: For those with excessive sweating, microneedling can help by reducing sweat gland activity when performed on the affected area.
Stretch Marks: Microneedling can stimulate collagen and elastin production in the dermis, making stretch marks less noticeable over time.
Overall Skin Rejuvenation: Beyond addressing specific concerns, regular microneedling sessions can contribute to overall skin rejuvenation, promoting a healthier and more youthful complexion.
Safety and Effectiveness
Microneedling is generally considered safe when performed by trained professionals using sterile equipment. Unlike more invasive procedures, it carries a minimal risk of infection or scarring. However, it’s crucial to follow post-procedure care instructions to ensure optimal results and minimize any potential side effects.
Microneedling has emerged as a versatile and highly effective therapeutic technique with a broad spectrum of applications. From addressing common dermatological concerns like wrinkles and scars to promoting hair growth and aiding in drug delivery, microneedling offers a simple yet transformative solution for those seeking to enhance their appearance and skin health. As technology and research continue to advance in this field, microneedling is likely to remain at the forefront of non-invasive skincare and cosmetic treatments.
Call (503) 272-6646 to schedule your appointment today or email admin@forestparkwellness.com.